Iran's Population - Shia And Sunni Communities Explored
Table of Contents
- The Roots of a Great Divide - Shia and Sunni History
- What is the main difference between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
- Iran's Religious Identity - The Shia and Sunni Population
- How many Shia and Sunni people live in Iran?
- A Closer Look at the Numbers - Shia and Sunni Demographics
- Are there concerns about the Shia and Sunni population growth in Iran?
- Historical Shifts and Current Realities - The Shia and Sunni Story in Iran
- Is the Shia government in Iran disadvantaging its Sunni population?
The Roots of a Great Divide - Shia and Sunni History
To really get a feel for the religious picture in Iran, it's helpful to go back to the very beginning of Islam itself. You see, the large division between what we now call Shia and Sunni Muslims didn't come about because of big differences in core beliefs about God or the Prophet. No, that's actually not the reason. Both groups, it turns out, hold very similar fundamental ideas about the oneness of the Creator, the role of prophets, and the sacred text, the Holy Quran. They both believe in the finality of Prophet Muhammad's message, which is pretty important. So, what was it that caused this significant split, then? Well, it was mostly, perhaps, a disagreement over who should lead the Muslim community after Prophet Muhammad passed away. This was a political question, rather than a theological one, you know, and it set the stage for everything that followed.
The group that would come to be known as Shia, which actually means "adherents of Ali," believed that Prophet Muhammad had chosen Ali ibn Abi Talib, his son-in-law and cousin, to take on the leadership role. This belief is a very central part of their identity. They feel that religious guidance should come from Muhammad's own family, a line of chosen individuals known as Imams. This connection to the Prophet's family is a deeply spiritual and historically rich part of their faith. It's a story that includes powerful moments, like the tragedy of Karbala, which is a really significant event for them. This particular branch of Islam, you see, holds that Ali was the rightful successor, designated by the Prophet himself. This conviction, then, is a cornerstone of their religious outlook and practice.
What is the main difference between Shia and Sunni Muslims?
The key distinction, then, between these two major branches of Islam, the Shia and the Sunni, truly comes down to the question of who should have been the leader right after Prophet Muhammad's passing. The Shia believe, quite firmly, that Muhammad had appointed Ali ibn Abi Talib to guide the community. This idea of a divinely appointed successor from the Prophet's own family is pretty central to their way of thinking. They follow the teachings of Muhammad and the spiritual direction provided by his family members, who they regard as Imams. This is a very specific and meaningful aspect of their faith, as a matter of fact.
On the other side, the Sunni tradition, which represents the larger portion of the global Muslim population, believes that leadership should have passed to the most capable individual chosen by the community, not necessarily someone from the Prophet's direct lineage. They followed a different path for selecting leaders, and this difference in succession is what created the initial separation. So, while both groups share a core set of Islamic beliefs, like the oneness of God and the importance of the Prophet, their paths diverged quite early on over this matter of who should hold the reins of the Muslim community. This is, you know, the fundamental point of departure between them.
Iran's Religious Identity - The Shia and Sunni Population
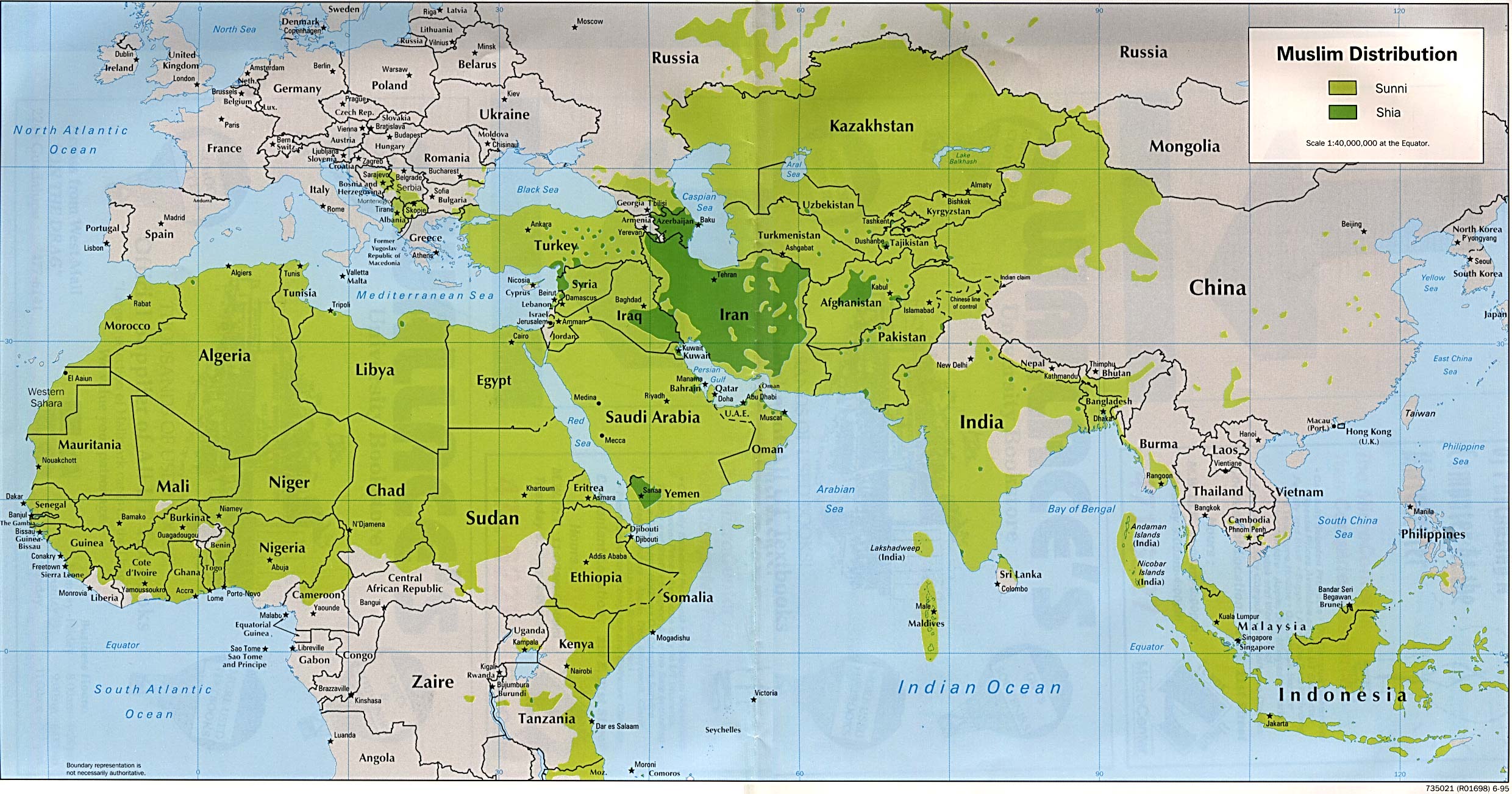
When we look at Iran today, it's pretty clear that Shia Islam is the dominant form of faith there. In fact, it's the official state religion, which is a rather significant detail. The vast majority of people living in Iran identify as Muslims, and within that group, the overwhelming portion belongs to the Ithnā ʿasharī, or Twelver, Shiʿi branch. This makes Iran quite unique on the world stage, as it's the only country that is officially a Shi'ite nation. This wasn't always the case, though; Iran was initially a Sunni-majority land, but that changed significantly over time. It's almost as if the country's religious landscape was completely reshaped by historical events, particularly the rise of certain ruling families.
The historical transformation of Iran's religious makeup is a fascinating story. During the 16th century, the Safavid dynasty came into power in Iran, and they initiated a big push to convert the Iranian people to Shia Islam. This was, you know, a campaign of forced conversion aimed at replacing the existing Sunni traditions, especially the Shafi'i school of thought, with Shia beliefs. This historical shift is a key reason why Iran looks the way it does religiously today. It's not just a matter of people choosing their faith; it was, in a way, a top-down change that reshaped the entire religious fabric of the nation. So, this historical context is really important for grasping the current situation regarding the Shia and Sunni population in Iran.
How many Shia and Sunni people live in Iran?
Let's talk about the numbers, because they paint a pretty clear picture of the religious landscape in Iran. According to figures from 2020, about 98.5 percent of the entire Iranian population saw themselves as Muslim. That's a really high percentage, you know, showing just how central Islam is to the country. Within that large Muslim group, a very substantial portion, around 81 percent, identified as Shia Muslims in that same year. This means that a much smaller share of the population followed the Sunni branch of Islam. It's pretty striking how dominant Shia Islam is when you look at these figures, as a matter of fact.
More recent data, like the 2016 Iranian census, also backs this up, showing that 99.4 percent of Iran's population is Muslim. And within that, Shia Muslims make up the vast majority, with something like 92.2 percent of all the Muslim people in the country belonging to this particular sect. It's also worth noting that more than a third of all the world's Shia Muslims actually make their home in Iran. This really underscores Iran's unique role as a major center for Shia Islam globally. While most countries in the Middle East have a Sunni majority, Iran, along with Iraq, stands out as having a Shia majority, which is, you know, quite distinctive.
A Closer Look at the Numbers - Shia and Sunni Demographics
Digging a bit deeper into the population figures for the Shia and Sunni communities in Iran, we see a very clear pattern of Shia dominance. As mentioned, the numbers consistently show that Shia Muslims form the overwhelming majority. This is quite different from many other places in the broader region, where Sunni populations are typically the larger group. For instance, while Iraq also has a Shia Muslim majority, Iran has the largest overall number of Shia Muslims anywhere in the world. This means Iran is, in a way, a global hub for Shia Islam, housing a significant portion of its followers. It's a rather important demographic detail that shapes many aspects of Iranian society and its interactions with other nations.
It's also interesting to consider the distribution of these populations within Iran itself. While the overall picture is one of Shia majority, there have been times and places where the populations of Shia and Sunni were more mixed. For example, the first Zaidi state, which is a branch of Shia Islam, was established in areas like Daylaman and Tabaristan in northern Iran. This shows that the religious landscape has had its variations over history, even if the general trend points towards a strong Shia presence today. The presence of groups like the Kurds and Turkmen, too, suggests that there are pockets of different religious affiliations, likely contributing to the Sunni minority within the country. So, the picture is, you know, not entirely uniform across all regions.
Are there concerns about the Shia and Sunni population growth in Iran?
There's been some talk, apparently, about the growth rates of the Shia and Sunni populations within Iran, and it's a topic that has sparked a bit of speculation. Some observers, it seems, have suggested that Iran's supreme leader might have concerns about the Sunni population potentially growing at a faster rate than the Shia one. The idea is that there might be a noticeable difference in how quickly these two groups are expanding. For example, some figures have pointed to a growth rate of around 7% in areas with a higher Sunni presence, compared to what might be a slower pace for the Shia population. This kind of demographic trend, you know, could naturally lead to discussions about future population balances and what that might mean for the country's overall religious makeup.
If these speculated growth differences are indeed accurate, it could, in a way, influence various policies or discussions within the country. A new policy, for instance, might be seen by some as an attempt to address these perceived demographic shifts. It's important to remember, though, that these are often speculations or arguments put forth by certain analysts, and the exact motivations behind any policy are not always openly stated. But the very existence of such discussions indicates that population dynamics, especially concerning the Shia and Sunni groups, are topics of interest and, perhaps, a little bit of concern for some within Iran. This shows that demographic trends are, you know, always a subject of close watch in any nation.
Historical Shifts and Current Realities - The Shia and Sunni Story in Iran
The story of Shia and Sunni populations in Iran is deeply tied to the country's past, particularly the significant changes that occurred centuries ago. As we've touched upon, Iran wasn't always a Shia-majority nation. The shift came about in a very deliberate way, especially with the rise of the Safavid dynasty in the 16th century. This period marked a major turning point, as the Safavids actively worked to establish Shia Islam as the dominant faith. This historical campaign of conversion really cemented the Shia identity of the country, shaping its religious landscape for centuries to come. It's almost as if the very identity of Iran became intertwined with its Shia faith during this time, creating a strong national character that persists today.
Today, Iran stands as a prominent example of a Shia-majority country, especially when compared to most other nations in the Middle East, which are primarily Sunni. This unique position means that Iran holds a special place for many Shia Muslims around the world. While there are other countries with significant Shia populations, such as Iraq, Bahrain, Azerbaijan, and, by some accounts, Yemen, Iran has the largest number of Shia Muslims. There are also notable Shia communities in places like Afghanistan, India, and Kuwait. This distribution shows that while Shia Islam is a global phenomenon, Iran is, you know, a very important center for it, both historically and in the present day.
Is the Shia government in Iran disadvantaging its Sunni population?
There's a point of view, put forward by some analysts, that suggests Iran's Shia government might be intentionally putting its Sunni citizens in a less favorable position. This argument proposes that there could be a deliberate and systematic approach to keep the Sunni minority at a disadvantage. It's a serious claim, naturally, implying a policy that might affect opportunities or treatment for Sunni individuals within the country. This kind of perspective often arises when looking at the relationship between a majority religious group and a minority one, especially when the majority group holds political power. So, it's a question that, you know, comes up in discussions about human rights and minority protections.
However, it's also important to consider the other side of this discussion. The available information suggests that there is, in fact, very little solid proof to back up the idea that Iran's government is systematically disadvantaging its Sunni citizens. While some analysts might voice these concerns, the evidence to support such widespread and deliberate policies appears to be quite limited. This doesn't mean that individual instances or challenges don't exist, but it does suggest that a broad, intentional government strategy of disadvantage might not be clearly demonstrable. So, while the question is raised, the supporting evidence for it is, you know, pretty sparse at this point.


Detail Author:
- Name : Mrs. Natalia Wiza III
- Username : marlene57
- Email : pkeeling@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1994-08-08
- Address : 4762 Kautzer Ramp Suite 288 West Jordymouth, MI 14252-0022
- Phone : +1-848-243-5033
- Company : Labadie, Wintheiser and Frami
- Job : Producers and Director
- Bio : Error adipisci et a eaque. Totam qui ea earum quis exercitationem quo. Omnis consequatur architecto et optio aut molestiae aut. Dolor vel est quas consequatur aut id aliquid.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/hermanc
- username : hermanc
- bio : Et quaerat nemo perspiciatis distinctio qui blanditiis nulla. Quos nesciunt ea autem aliquid molestiae qui nisi. Minima est ut asperiores id ut nobis veniam.
- followers : 6811
- following : 2951
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/herman2003
- username : herman2003
- bio : Voluptatum aliquam illo in mollitia id minus.
- followers : 1213
- following : 2595
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/cherman
- username : cherman
- bio : Consequatur ut sed dolorem ut ex ut.
- followers : 3405
- following : 2869
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@herman1988
- username : herman1988
- bio : Ad commodi harum ut adipisci sunt occaecati a.
- followers : 2202
- following : 1499
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/chandler4234
- username : chandler4234
- bio : Et sit et veritatis molestiae cum in voluptates. Sit perferendis accusamus qui qui rerum sed.
- followers : 2934
- following : 1700